Prostatitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease, which is considered one of the most common, but at the same time, poorly studied and poorly amenable to conservative correction, pathologies with a severe urodynamic disorder.The incidence of prostatitis in recent decades has been higher in men who are in the stage of active reproduction (age group from 20 to 45 years) and who are sexually active, although until recently it was believed that the maximum risk of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland exists only in older and elderly men.
In most cases, acute inflammation of the prostatic glands develops against the background of massive contamination of the mucous membranes of the prostate with pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms: gonococci, staphylococci, E. coli, etc.
In addition to antibiotics, which are used both in the acute phase of the disease and for the treatment of recurrent forms of infectious prostatitis (including CPPS - chronic pelvic pain syndrome), complex therapy for inflammatory changes in the interstitial and parenchymal tissue of the gland also includes the use of modern methods, for example, laser therapy, cryodestruction or pulsed microcurrents.In order for the treatment to be effective and achieve stable remission, the man will also have to adjust his regimen, diet and lifestyle.
Basic therapy for infectious inflammation
The main goal of therapy in the treatment of any form of prostatitis is to stop inflammation and eliminate inflammatory changes, as well as relieve pain, the prevalence of which, according to various sources, ranges from 35% to 67% (approximately every second man suffering from prostatitis complains of pain as a dominant symptom).In acute cases, the use of massive antibacterial therapy allows you to quickly achieve a clinically significant effect, which occurs within 4-5 days.Despite the rapid relief of the condition with infectious inflammation of the prostate, it is impossible to stop treatment with antibiotics, since most typical pathogens of genitourinary infections very quickly develop resistance to drugs of this group, and discontinuation of therapy will lead to chronicity of the disease.
Some of the main causative agents of prostatitis - fecal staphylococcus and Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) - even if the conditions of administration and continuous use of antibiotics are met, they are capable of creating a thick film capsule around the membrane membrane, which reduces the bioavailability of the drugs used and increases the resistance of bacteria to the selected group of antibiotics.For this reason, it is recommended to continue antibiotic therapy even if a positive result is quickly achieved for at least 4 weeks.
Why you can’t choose an antibiotic yourself
Antibiotics are the basis for the treatment of acute infectious prostatitis, but they must be prescribed by the attending physician after laboratory examination of prostatic secretions, taking into account several factors: the type of pathogen identified, the degree of contamination of the mucous membranes, and the resistance of a particular microorganism to certain groups of antibiotics.Experts in the field of practical urology also note that in recent years there has been a steady increase in mixed genitourinary infections, so combinations of several antibacterial and antimicrobial agents are often used to treat acute prostatitis.
Self-medication of acute prostatitis in almost 60-70% of cases leads to the infection becoming chronic, which is a very high rate and confirms the inadmissibility of independently choosing medications and ignoring medical prescriptions.The importance of undergoing laboratory and physical diagnostics, as well as consultation with a specialist, before using antibiotics is due to the following points.
- Bioavailability indicators.Some antibacterial drugs (for example, the most popular and prescribed antibiotics - drugs of the penicillin group) have a low degree of penetration into the prostate tissue, so their use for prostatitis is ineffective and impractical.Almost all aminoglycosides also have poor bioavailability.
- Degree of bactericidal effect.In case of acute damage to the prostatic glands, antibiotics with a bactericidal effect should be chosen, which cause the death of the infectious pathogen.In chronic cases, it is more advisable to prescribe drugs with a bacteriostatic effect, stopping the growth of pathogenic flora and preventing its reproduction.
- General condition of the patient.Patients with severe immunosuppression, as well as severe manifestations of febrile and intoxication syndrome should be treated in a hospital setting.Antibiotics are administered intravenously to such patients (oral dosage forms are ineffective in severe clinical cases).
Pay attention!The absence of a positive effect during the use of antibacterial therapy may indicate the development of a prostate abscess.This is an acute pathology that requires emergency hospitalization of a man in a hospital and surgical opening of the abscess, followed by drainage and antiseptic treatment of the cavity.
Modern methods of treating chronic inflammation
Physiotherapy is a medical branch that studies and applies for therapeutic purposes various natural factors (including artificially created ones) that have a positive effect on the human body.In the complex treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system, physiotherapy is used at the recovery stage, after relief of acute symptoms.
The main goal of physiotherapy is to eliminate residual inflammatory effects and stimulate the restoration of damaged tissues.A course of physiotherapeutic treatment usually consists of 5-10 procedures lasting 10-15 minutes.To achieve a positive result (reducing the frequency and intensity of chronic pelvic pain, normalizing urination, improving the rheological properties of prostatic secretion, etc.) several courses may be required.
Low-level laser therapy
Laser therapy is one of the most effective and popular methods of treating chronic inflammation of the prostate in men, which is most often used as an adjuvant after primary drug correction.The basis of laser therapy is the use of optical range emitted by a special device - a laser.The laser can operate in pulsed and continuous pulsed mode, and the wavelength can reach up to 904 nm. Rarely in urology is the method of intravenous laser illumination of blood used, which is considered by many experts to be the most effective and universal method of complex treatment of many urological diseases.
The main advantages of laser therapy are its fairly high efficiency, painlessness, and stimulation of not only damaged but also nearby tissues.This method of physiotherapy is especially useful for congestive (stagnant) prostatitis, since laser radiation has a positive effect on microcirculation in the pelvic vessels and normalizes the outflow of secretions from the prostatic glands.
Electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation with currents is indicated for the treatment of any form of prostatitis, accompanied by erectile dysfunction and a general decrease in potency.Stimulation is carried out using the endourethral method, that is, a catheter with an electrode attached to it is inserted directly into the back of the urethra, where the prostate is located.In some cases, rectal electrodes can be used for treatment, which provide electrical stimulation of the prostate gland in the place where it borders the anterior ampulla of the rectum.In both cases, it is important that the bowels and bladder are empty.
Treatment with electric currents has a complex positive effect on the prostatic glands, namely:
- eliminates stagnation of fluids (blood and lymph) in the pelvic organs;
- ensures normal outflow of prostatic secretions;
- increasing the permeability of cell membranes of the parenchymal tissue of the gland and its interstitium, which promotes faster absorption of drugs into the tissue of the inflamed prostate;
- reduces swelling;
- normalization of muscle tone of the pelvic muscles;
- increasing the regenerative ability of cells and local immunity (especially in chronic bacterial prostatitis).
The therapeutic effect after electrical stimulation of the prostate occurs after 2-3 procedures, but it is important not to stop treatment in order to minimize the risks of a possible relapse.A full course usually consists of 5-7 procedures.
Pay attention!Prostate stimulation with electric currents is especially effective for prostatitis with severe erectile disorders.
Thermotherapy
Thermotherapy is also a type of physiotherapy and can be used for self-treatment of prostatitis or used in specialized physiotherapy rooms.Heat sources for warming up the prostate gland can be:
- mineral applications (bischofite, paraffin, ozokerite);
- special electric lamps;
- heating pads (water, electric);
- devices for infrared irradiation.
In day hospitals and physiotherapy rooms, reflectors are often used to warm the prostate, which are an incandescent lamp with a focusing lampshade (“blue lamp”).The procedure has certain contraindications, for example, disorders of the autonomic nervous system, malignant tumors, acute infectious-inflammatory and purulent-infectious processes, active forms of tuberculosis.The use of thermal procedures in the acute period of the disease is unacceptable, as this can lead to hematogenous infection of neighboring organs and tissues (due to a sharp increase in blood circulation) and the development of serious complications, including septic blood poisoning.
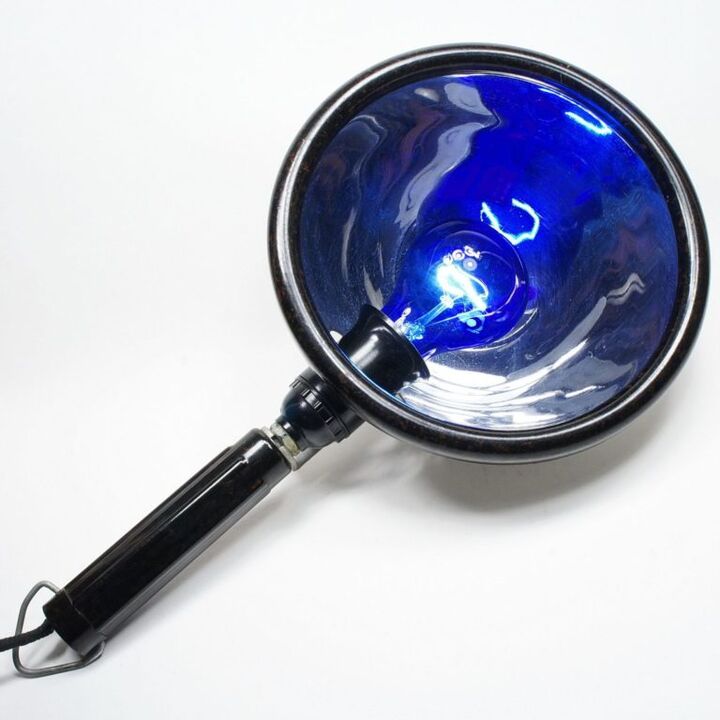

Important!If a man is prescribed hormonal or immunomodulatory therapy, it is necessary to consult with a doctor about the possibility of using thermal procedures (especially if the patient is being treated at home).It is unacceptable to prescribe thermal procedures with cytostatics and hemostatic drugs.
Ozone therapy
This is a fairly effective modern method of treating prostatitis, practiced mainly in paid medical centers.Medical ozone is produced by special medical devices called ozonizers.The gas in its pure form is highly toxic and, if inhaled, can cause acute chemical poisoning and death.To introduce ozone into the patient’s blood, the gas is mixed with blood or saline (salt concentration 0.9%).
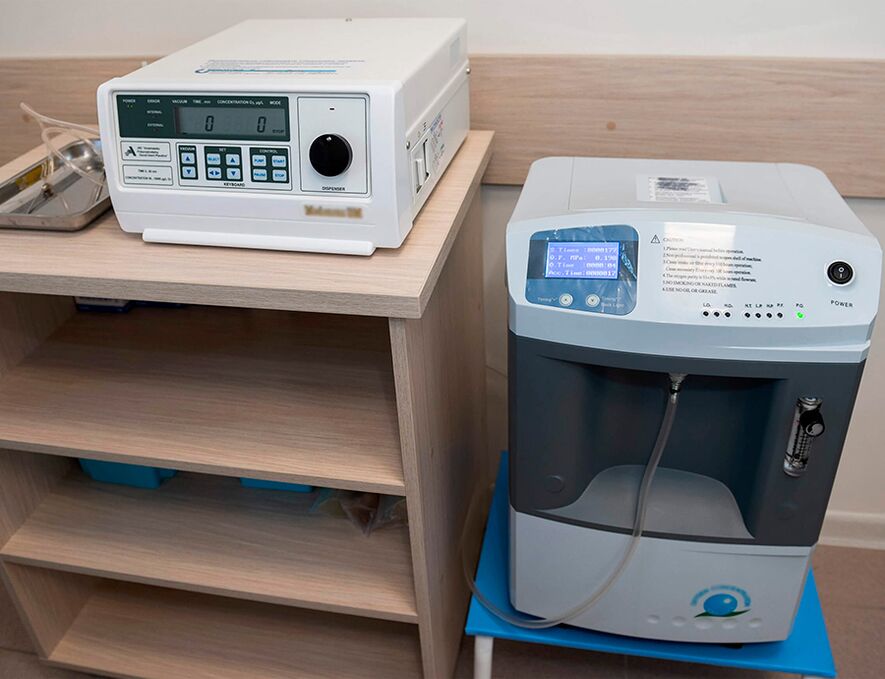

The main indication for the use of ozone therapy for inflammation of the prostate gland is chronic infectious prostatitis with frequent relapses (more than 2-3 times a year).Ozone has powerful antiseptic and bactericidal properties, therefore it is often used to disinfect premises, including industrial premises.It destroys almost all strains of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, which most often cause inflammation of the prostate and are highly resistant to antibacterial drugs.The feasibility of using this method is considered justified if the patient does not experience stable positive dynamics after changing three antibiotics.
The ozone solution is injected using a special catheter into the prostatic part of the urethra or rectum.The course consists of 5-10 procedures.
Devices for the treatment of prostatitis
Hardware treatment of prostatitis can be carried out both in a physiotherapy room and at home (strictly after consultation with the attending physician).Many of them are devices for rectal use, so in addition to the main contraindications directly related to the disease, it is important to take into account local restrictions: acute stage of hemorrhoids, anal bleeding of unknown origin, violation of the integrity of the epithelial lining of the rectum, proctitis and paraproctitis.
It is unacceptable to introduce any foreign objects (electrodes, sensors) into the rectum in case of rectal prolapse, pelvic abscesses, thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins and congenital immaturity of the innervation apparatus of the large intestine.
Important!Before using any devices for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma, you should consult your doctor, since some of these devices may not only be useless, but also significantly harm your health.Hardware effects on prostate tissue are unacceptable in the acute period of the disease, as well as in the presence of any possible contraindications (listed above).
Prostatitis is a serious disease that requires an integrated approach to treatment.In addition to medication and physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of prostatitis, in some cases it is necessary to use psychocorrection, as well as correction of lifestyle, eating habits, work and rest patterns.Basic therapy during the recovery and rehabilitation period should be supplemented by auxiliary treatment methods: hirudotherapy (leech treatment), balneotherapy (mineral water therapy), mud therapy, exercise therapy.A man should also move enough, give up bad habits, and monitor his psycho-emotional state.Outside periods of exacerbation, annual sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated to consolidate the achieved result.